 |
| What is the thin element that glows inside light bulbs |
What is the thin element that glows inside light bulbs
There is no doubt that you have seen a thin wire glowing inside old electric bulbs, which are known for consuming more electrical energy—around 100 watts—compared to modern energy-saving LED bulbs. But what is the name of the thin electrical wire found in old incandescent light bulbs?
What is the name of the thin wire inside the bulb:
This wire is called the tungsten filament. It is a thin wire known for its ability to withstand extremely high temperatures, reaching up to 3,422°C. Its chemical symbol is W, and its atomic number is 74. Originally, tungsten is a heavy mineral that was discovered by the chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele.
The tungsten filament is placed inside the traditional glass bulb along with noble gases, primarily argon gas. When an electric current passes through the filament, it glows, producing light due to the movement of particles within this electrical conductor.
Tungsten metal image :
 |
| Tungsten |
Components of the Old Electric Bulb:
The structure of incandescent light bulbs is shown in the figure below:
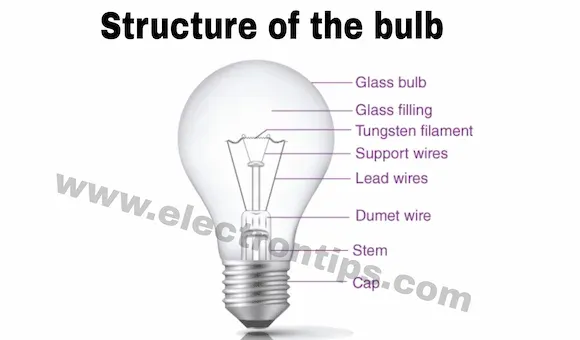 |
| Structure of the bulb light |
Why Does the Incandescent Light Bulb Consume a Lot of Energy:
Old incandescent light bulbs consume a significant amount of energy because they convert a large portion of electrical energy into heat energy, causing the bulb to heat up and leading to high energy consumption.
Although traditional incandescent bulbs consume a lot of electricity, they have played a crucial role in illuminating streets and homes worldwide. Today, more advanced lighting technologies exist, such as LED bulbs, fluorescent lamps, and other energy-efficient lighting solutions.
